CarTech CTS XHP alloy is powder metallurgy, air-hardening, high carbon, high chromium, corrosion-resistant alloy. It can be considered either a high hardness 440C stainless steel or a corrosion-resistant D2 tool steel. CarTech CTS XHP alloy possesses corrosion resistance equivalent to CarTech 440C stainless steel and can attain a maximum hardness of 64 HRC.
In addition, the composition of CarTech CTS XHP alloy has been balanced so that it can attain a minimum hardness of 60 HRC when air cooled from hardening temperatures of 1850 to 2000 °F (1010 °C to 1093 °C). CarTech CTS XHP alloy is thus more forgiving during heat treatment than similar alloys.
CTS-XHP steel is a stainless steel from Carpenter Metal Solutions, Inc. in the USA. It is manufactured using the Micro-Melt (MM) technology developed by the company, the advantage of which is reduced grain, improved viscosity, good wear resistance and machinability, and high corrosion resistance properties. The steel has received well-deserved recognition among manufacturers of all kinds of knives and surgical instruments.
Applications
CarTech CTS XHP can be used for specialty knives where the alloy's fine carbide distribution can be used to produce a keenly sharp cutting edge. The material can be easily ground to the thin profiles required for cutting tools. CarTech CTS XHP knife blades can be finely polished to high luster or produced with a uniform matte finish.
Corrosion resistance
Carpenter CTS XHP alloy possesses corrosion resistance equivalent to Type 440C stainless. CTS XHP alloy resists corrosion in normal domestic environments and very mild industrial environments, including many petroleum products and organic materials. For optimum corrosion resistance, surfaces must be free of scale and foreign particles and finished parts should be passivated.
Chemical composition
Chemical composition of steel grade CTS-XHP | |||||||
| C | Cr | Mo | V | Mn | Si | Ni | Fe |
| 1,6 | 16,0 | 0,80 | 0,45 | 0,50 | 0,40 | 0,35 | Other |
Physical properties
- Density: 7.62 g/cm³;
- Mean сoefficient of thermal expansion (CTE):
Annealed condition.
Mean coefficient of thermal expansion - Carpenter CTS XHP | |||
| Room temperature | Average coefficient | ||
| 77 °F to | 25 °C to | 10-6 / °F | 10-6 / °C |
| 212 | 100 | 5.65 | 10.17 |
| 392 | 200 | 6.02 | 10.83 |
| 572 | 300 | 6.24 | 11.23 |
| 752 | 400 | 6.40 | 11.52 |
| 932 | 500 | 6.53 | 11.76 |
| 1112 | 600 | 6.63 | 11.93 |
| 1292 | 700 | 6.71 | 12.13 |
| 1472 | 800 | 6.87 | 12.37 |
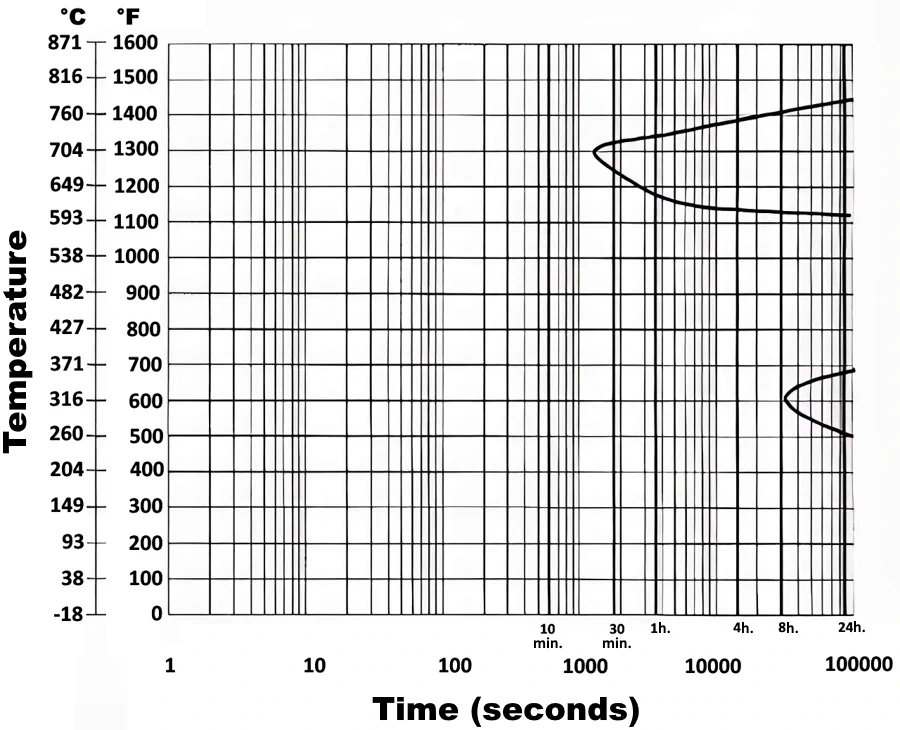
Isothermal transformation (I-T) diagram - Carpenter CTS XHP Alloy.
Austenitize at 1925 °F (1052 °C) for 25 mins., quenched to I-T temperature, then brine quenched to room temperature.
Mechanical properties
Hardened & tempered properties.
Compression test results - Carpenter CTS XHP. Compressive yield strength is 347.0 ksi, compressive modulus is 32.6 x 10^6 psi, heat treat is 1925 °F (1052 °C) (25 mins.) O.Q. + -100 °F (-73 °C) (1h) A.W. + 350 °F (177 °C) (1h) A.C.
Typical annealed tensile properties - Carpenter CTS XHP
| Yield strength | Ultimate tensile strength | Elongation % | Reduction in area % | Hardness BHN | ||
| ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | |||
| 68.3 | 471 | 125.3 | 864 | 10.2 | 16.0 | 230/255 |
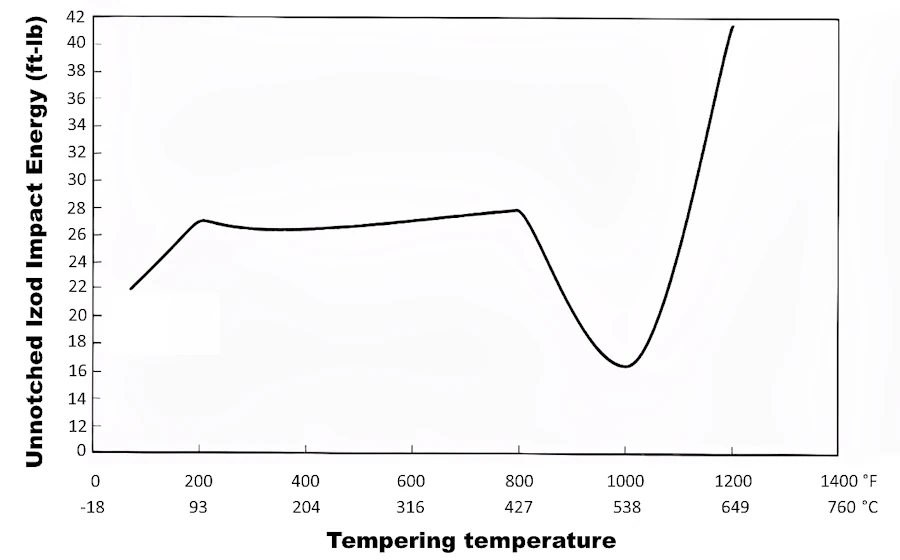
Unnotched Izod Impact Energy - Carpenter CTS XHP
Austenitized 1925 °F (1052 °C), 25 mins., AC and tempered for 1 hour.
Heat Treatment
Decarburization
Carpenter CTS XHP alloy, like all high carbon tool steels, is subject to decarburization during thermal processing and precautions must be taken to control this condition.
Annealing
Carpenter CTS XHP alloy should be annealed in a neutral atmosphere. Heat uniformly to 1550/1600 °F (843/871 °C), then cool very slowly in the furnace at a rate of not more than 20 °F (11 °C) per hour until the furnace is black. The furnace may then be turned off and allowed to cool naturally. Annealed hardness is 230/255 HBN.
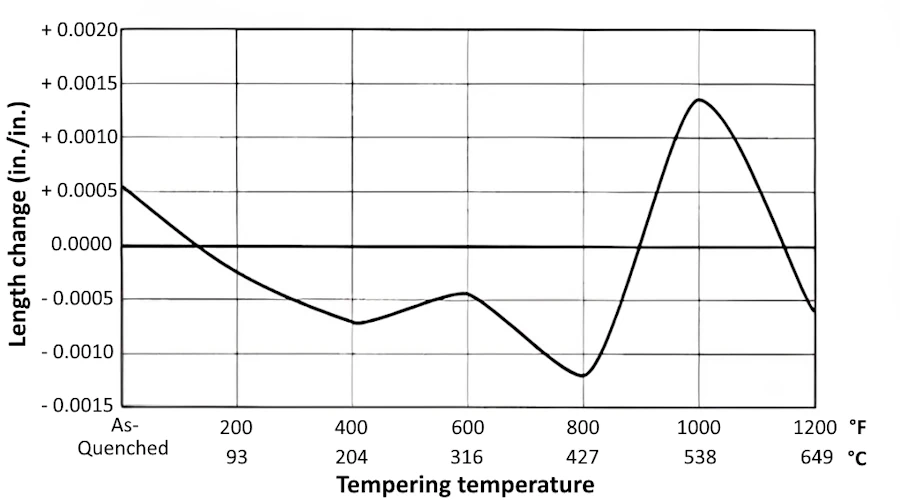
Size change in hardening
Air quenched from 1925 °F (1052 °C), ternpered 1 hour at temperature.
Effect of refrigeration on as-hardened condition
- Hardness measurements are averages rounded to nearest 0.5 HRC;
- Sample size: 1 in. dia. x 0.5 in. thick.
Heat treatment: 25 minutes at hardening temperature, than air cooled or oil quench to room temperature. Leave as-hardened, or refrigerate at -100 °F (-73 °C) for 1 hour. Air warm to room temperature.
| Hardening Temperature | Air Cool Only | Air cool + Refrigeration | Oil Quench Only | Oil Quench + Refrigeration | |
| °F | °C | ||||
| 1850 | 1010 | 62.0 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 63.5 |
| 1090 | 1038 | 62.5 | 63.5 | 63.0 | 64.0 |
| 1950 | 1066 | 62.5 | 64.0 | 62.5 | 64.5 |
| 2000 | 1093 | 58.5 | 64.0 | 57.0 | 64.0 |
Effect of refrigeration on tempered hardness
- Hardness measurements are averages rounded to nearest 0.5 HRC;
- Sample size: 1-in. dia. x 0.5 in. thick.
Heat treatment: 25 minutes at hardening temperature. Air cooled or oil quench. Leave as-hardened, or refrigerate at -100 °F (-73 °C) for 1 hour. Air warm. Temper 1 hour at temperature. Air cool.
| Tempering Temperature | Air Cool Only | Air cool + Refrigeration | Oil Quench Only | Oil Quench + Refrigeration | |
| °F | °C | ||||
| 1900 °F (1038 °C) Hardening Temperature | |||||
| As-Hardened | 62.5 | 63.5 | 63.0 | 64.0 | |
| 200 | 93 | 63.0 | 64.0 | 63.0 | 64.0 |
| 250 | 121 | 63.0 | 64.0 | 63.0 | 64.0 |
| 300 | 149 | 62.0 | 63.0 | 62.0 | 63.0 |
| 350 | 177 | 61.0 | 62.0 | 61.0 | 62.0 |
| 400 | 204 | 60.5 | 62.0 | 60.5 | 61.0 |
| 450 | 232 | 60.0 | 61.0 | 59.5 | 60.5 |
| 500 | 260 | 59.0 | 60.5 | 59.0 | 60.0 |
| 600 | 316 | 58.0 | - | - | - |
| 800 | 427 | 58.0 | - | - | - |
| 1950 °F (1066 °C) Hardening Temperature | |||||
| As-Hardened | 62.5 | 64.0 | 62.5 | 64.5 | |
| 200 | 93 | 62.5 | 65.0 | 62.5 | 65.0 |
| 250 | 121 | 62.5 | 65.0 | 62.0 | 65.0 |
| 300 | 149 | 62.0 | 64.0 | 61.5 | 64.0 |
| 350 | 177 | 61.0 | 63.0 | 60.5 | 63.0 |
| 400 | 204 | 60.5 | 62.5 | 60.0 | 62.5 |
| 450 | 232 | 59.5 | 61.5 | 59.0 | 61.5 |
| 500 | 260 | 59.0 | 61.0 | 57.5 | 60.5 |
| 600 | 316 | 57.5 | - | - | - |
| 800 | 427 | 57.5 | - | - | - |
Workability
Forging
Carpenter CTS XHP alloy forges very much like high-speed steels. Preheat to 1400/1500 °F (760/816 °C), then heat slowly and uniformly to 1900/2100 °F (1038/1149 °C). Do not forge below 1700 °F (927 °C), and reheat as often as necessary. Cool in a furnace heated to about 1550 °F (843 °C), soak uniformly at this temperature, then shut off the heat and cool slowly in the furnace. Anneal after forging. Cool to room temperature before annealing.
Wear Resistance
The wear characteristics in the table below were generated using ASTM G65 Procedure "A", the Standard Practice for conducting Dry Sand/Rubber Wheel Abrasion Tests. The data are presented as volume loss as required by the ASTM Standard. It should be noted therefore that a lower number means better wear resistance.
| Wear resistance - Carpenter CTS XHP vs. 440 C vs. D2 | ||
| CTS XHP | 1925°F (1052°C) (25 mins.). Air cool/-100 °F (-73 °C)(1h). Air warm/350 °F (177 °C) (1h). Air cool. | |
| 440 C | 1900 °F (1038 °C) (25 mins.). Oil quench/-100 °F (-73 °C) (1h). Air warm/350 °F (177 °C) (1h). Air cool. | |
| D2 | 1850 °F (1010 °C) (25 mins.). Air cool-as hardened. | |
| Material | Hardness, HRC | Average ASTM Volume Loss (mm3) |
| CTS XHR | 62.5 | 35.1 |
| 440 C | 58.5 | 66.9 |
| D2 | 63.5 | 37.6 |
The information and data presented herein are typical or average values and are not a guarantee of maximum or minimum values. Applications specifically suggested for material described herein are made solely for the purpose of illustration to enable the reader to make his/her own evaluation and are not intended as warranties, either express or implied, of fitness for these or other purposes.